Essential Guide to Leatherback Sea Turtle Diet: Discover Their Incredible Feeding Habits in 2025
Overview of Leatherback Sea Turtle Diet
The leatherback sea turtle, a remarkable marine reptile, holds a crucial position within our ocean ecosystems. Understanding the leatherback sea turtle diet is essential for grasping their role in oceanic health. Leatherbacks differ from other sea turtles, primarily in their preference for jellyfish and other soft-bodied prey. Their specialized feeding habits not only cater to their nutritional needs but also affect the populations of jellyfish—a notable aspect of marine wildlife dynamics.
This article will explore the fascinating feeding habits of leatherback turtles, assess their key prey types, and detail various environmental factors that shape their diet. Additionally, by focusing on conservation efforts, we will highlight the need to protect these ancient reptiles against the backdrop of climate change and human impact.
Key takeaways include learning about their nutritional preferences, understanding threats to their survival, and appreciating their ecological significance. Gear up for a deep dive into the wonderful world of leatherback turtle nutrition!
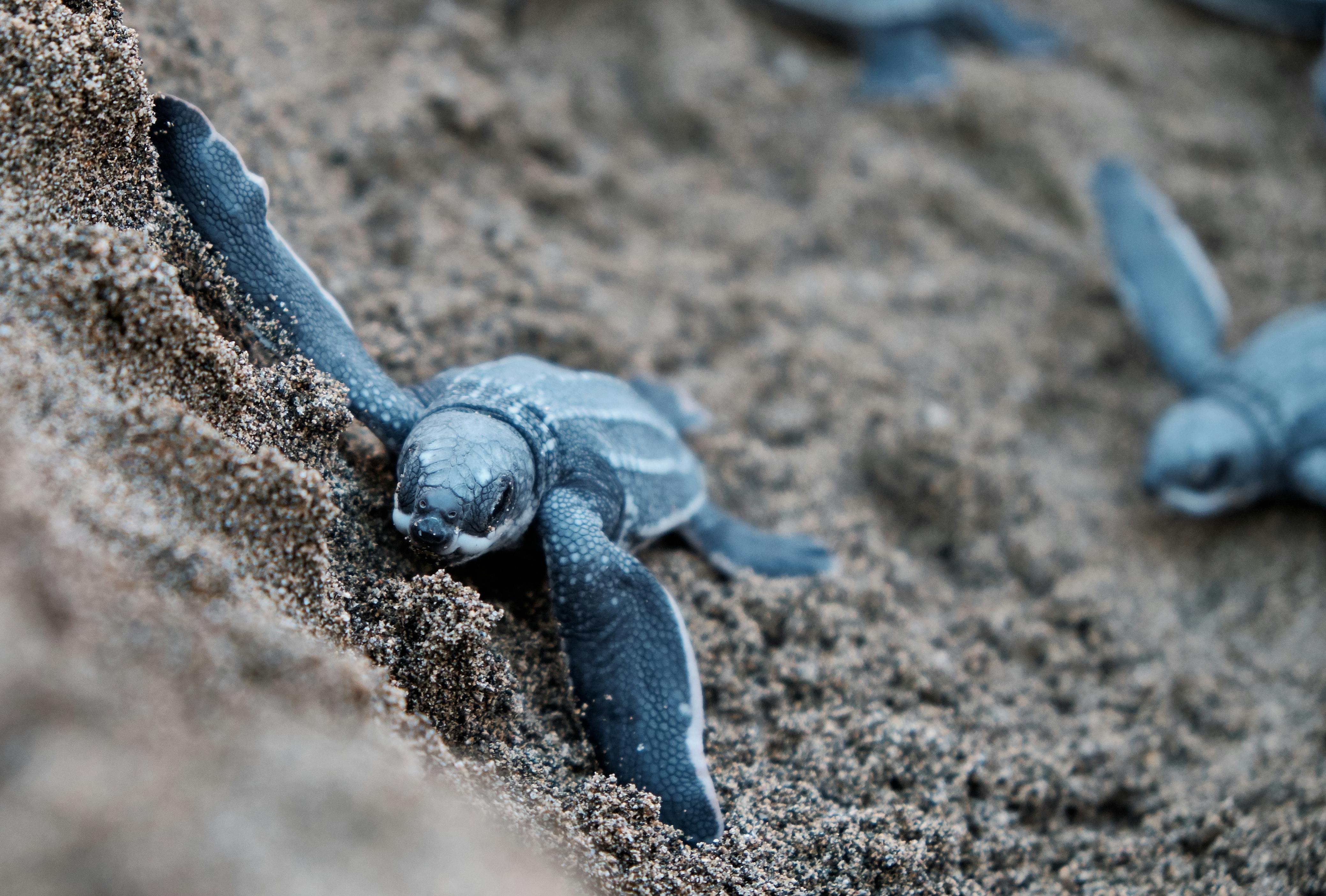

Key Components of Leatherback Turtle Nutrition
Understanding the leatherback turtle nutrition starts with recognizing what composes their diet. With a unique offense in the food chain, leatherbacks primarily feast on jellyfish, utilizing their incredible adaptations to capture their prey effectively. Additionally, they have been documented feeding on a variety of soft-bodied marine organisms, such as sea cucumbers and certain types of fish.
Moreover, the structure of their jaws, which lack a hard beak, enables them to consume large quantities of jellyfish efficiently. This diet not only satisfies their energy requirements—critical for survival and reproduction—but also ensures the balance within marine ecosystems.
Given their primary reliance on jellyfish, factors such as the abundance of jellyfish blooms directly influence leatherback foraging success. As environmental changes and ocean health fluctuate, awareness of how these shifts impact their food availability is crucial.
Another key aspect of leatherback nutrition is the oceanic diet leatherback turtles adopt, which showcases their adaptability to diverse marine habitats.
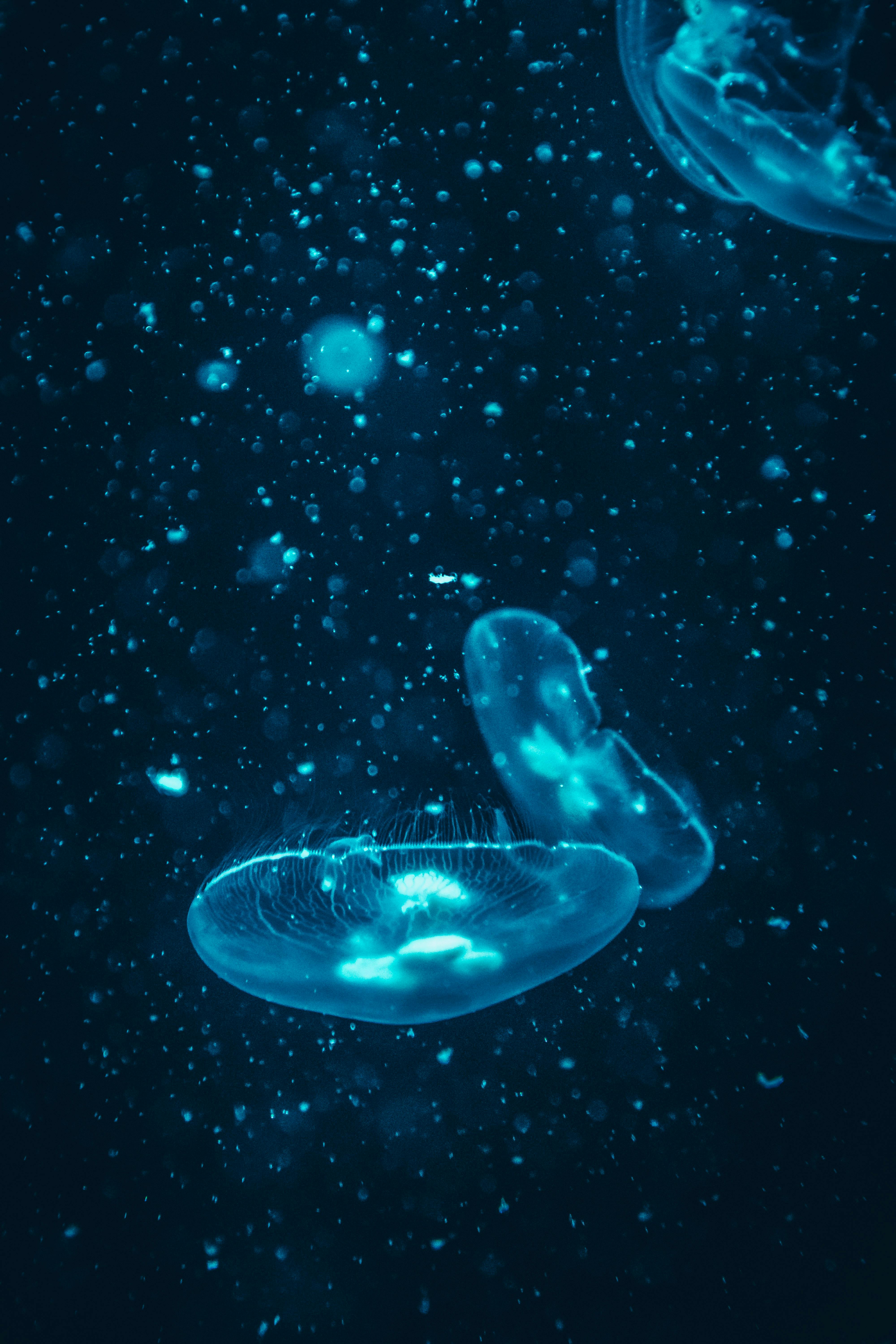
Jellyfish as Primary Food Source
Leatherback sea turtles are often referred to as the “jellyfish eaters” of the ocean. They exhibit specialized leatherback turtle feeding behavior, designed for the effective consumption of jellyfish, which form the bulk of their diet. Their body physiology allows them to consume large amounts of these oceanic creatures in one feeding session, making jellyfish both a critical and plentiful energy source.
Interestingly, studies have shown that jellyfish possess varying nutritional profiles, which can influence the feeding strategies of leatherback turtles. Different species of jellyfish have distinct protein and lipid compositions that can affect the overall growth and health of leatherbacks. Therefore, understanding these nutritional profiles enhances our comprehension of their feeding ecology.
Influences on Leatherback Turtle Feeding Strategies
Leatherback turtles are equipped with several remarkable adaptations that influence their feeding strategies. Their large size allows them to migrate vast distances in search of food, making them highly efficient predators in the ocean. The best leatherback turtle food preferences depend largely on the abundance of jellyfish in specific regions, leading them to shift their habitats accordingly based on seasonal fluctuations.
Research indicates that climate change and ocean pollution significantly affect jellyfish populations, which inevitably impacts leatherback feeding patterns. As jellyfish blooms increase in response to warmer waters and nutrient runoff, leatherbacks may experience both positive and negative repercussions in their foraging success.
Leatherback Turtle Foraging Behavior
To appreciate the leatherback turtle foraging behavior, we must observe their unique feeding mechanisms. They often foray through various oceanic habitats, employing strategies such as opportunistic feeding and selective hunting to capitalize on the abundance of prey.
For instance, leatherbacks commonly engage in continuous swimming while foraging, allowing them to encounter numerous jellyfish along the way. This behavior distinguishes them from other sea turtles that predominantly rely on sitting and waiting for prey as it passes.
Moreover, as they often dive deep into the ocean, leatherbacks can exploit higher concentrations of jellyfish. Their migratory patterns are strategically aligned with the natural rhythms of jellyfish blooms, highlighting the intricacies of their marine wildlife interactions.
Seasonal and Environmental Factors Influencing Diet
Seasonal shifts and environmental factors significantly affect leatherback feeding behavior. During warmer months, jellyfish populations tend to surge, which encourages greater foraging activity among the turtles. In areas where upwelling occurs, nutrient-rich waters fuel higher productivity and thus, directly enhance prey availability.
Furthermore, oceanic currents also contribute to the distribution of jellyfish, making certain regions more favorable for leatherback feeding. The turtles’ extensive migratory routes are typically influenced by currents that direct them toward abundant jellyfish, demonstrating a remarkable adaptation to evolving marine environments.
Challenges Facing Leatherback Turtle Feeding Ecology
Even as the leatherback turtles adapt to their environments, a variety of threats challenge their survival and the health of their feeding ecology. Predation from larger marine animals and human activities, including overfishing and pollution, pose critical risks to their food sources.
Moreover, human-induced climate change exacerbates threats to jellyfish populations, creating an unstable future for leatherbacks. With the potential for diminishing food resources, the conservation of leatherback sea turtles has become an urgent priority, aiming to secure their habitats and promote healthy marine ecosystems.
For conservationists, understanding leatherback turtle conservation issues and improving data from marine biology studies is vital to implement strategic measures that can protect these turtles against the myriad threats they face.
Impact of Pollution on Leatherback Diet
Ocean pollution significantly impacts leatherback turtles, both directly and indirectly. Ingesting plastic debris mistakenly believed to be jellyfish threatens their health—leading to severe injuries or even death. Moreover, the chemical pollutants concentrated within the ocean can deteriorate the quality of their preferred foods.
Awareness regarding this pollution’s impacts on leatherback turtle health is vital as we strive for healthier oceans and sustainable practices that protect marine life. The implementation of focused marine conservation campaigns is critical in addressing these impacts and advocating for clean ocean policies.
Conservation Efforts for Leatherback Sea Turtles
Conservation efforts targeting leatherback sea turtles are essential for ensuring their survival amid escalating threats. From introducing marine protected areas to enforcing regulations that limit fishing practices, these initiatives play a significant role in the well-being of leatherbacks.
Key components of turtle conservation programs involve educating communities about the significance of leatherback turtles in marine ecosystems. Furthermore, restoration projects that focus on habitat protection enable the preservation of critical nesting sites and feeding environments that support healthy leatherback populations.
Global Initiatives and Research on Leatherback Nurturing
International collaborations for turtle studies have emerged as indispensable tools for marine conservation. Tracking their migratory patterns using advanced technology has yielded significant insight into leatherback behaviors and habitat preferences. By sharing data across borders, researchers can better understand the ecological roles these magnificent creatures play in ocean health.
Furthermore, integrating community engagement into conservation programs enriches public awareness and fosters a collective responsibility toward marine biodiversity. Involvement in marine conservation areas underlines the importance of continuous support for protective measures aimed at preserving the leatherback population.
Conclusion and Future Perspectives
The leatherback sea turtle is a remarkable emblem of oceanic health, and understanding their complex diet provides valuable insights into the intricate mechanics of marine ecosystems. As challenges continue to emerge, our commitment to their conservation is more important than ever. The future of leatherback turtles hinges on collaborative efforts to protect their habitats and ensure sustainable feeding opportunities. By nurturing our oceans, we play a crucial role in safeguarding not just the leatherbacks, but the entirety of marine life.
Q&A Section
Q: What do leatherback sea turtles eat?
Leatherback turtles mainly consume jellyfish but can also eat other soft-bodied marine organisms such as sea cucumbers and fish.
Q: How do human activities impact leatherback turtles?
Human impacts such as pollution, overfishing, and climate change threaten leatherback turtles by disrupting their feeding ecology and habitat.
Q: What conservation efforts are necessary for leatherback turtles?
Conservation initiatives should focus on protecting nesting sites, addressing pollution, and promoting awareness of sustainable marine practices.
Q: How do climate changes affect the leatherback turtle diet?
Climate change influences jellyfish populations, causing fluctuations in availability which directly impacts the feeding success of leatherback turtles.
Q: Are leatherback turtles endangered?
Yes, leatherback turtles are classified as an endangered species due to declining populations and threats from human activities.
