“`html
Best 5 Ways to Calculate the Area of a Pyramid
Understanding how to calculate the area of a pyramid is essential for anyone studying geometry, whether it’s for academic purposes, architectural designs, or practical applications. In 2025, as we continue to explore innovative methods and techniques, we must grasp the underlying techniques to find the relevant area formulas. This article offers detailed descriptions of the best ways to calculate the area of pyramids, focusing on different types of pyramids and their unique properties.
Pyramid Geometry: Fundamental Concepts
Before diving into calculations, it’s crucial to understand the basic geometry of pyramids. A pyramid is a three-dimensional shape consisting of a polygonal base and triangular faces that converge at a single point called the apex. The height of a pyramid is the perpendicular distance from the apex to the base plane, while the base area can vary, resulting in different types of pyramids such as triangular, square, or rectangular base pyramids. Mastering the geometry of pyramids provides the foundation for effectively calculating their areas.
Calculating the Base Area of the Pyramid
To determine the total area of a pyramid, one must first calculate its base area. Depending on the shape of the base, you’d use different formulas:
- For a square base: Area = side × side
- For a rectangular base: Area = length × width
- For a triangular base: Area = (base × height) / 2
This foundational step is crucial since the base area contributes significantly to the overall surface area and volume of the pyramid. Knowing how to compute these areas accurately can assist in various applications, from architectural designs to CAD modeling. If you encounter irregular shapes, consider dividing the base into simpler geometric forms to apply the standard area formulas accordingly.
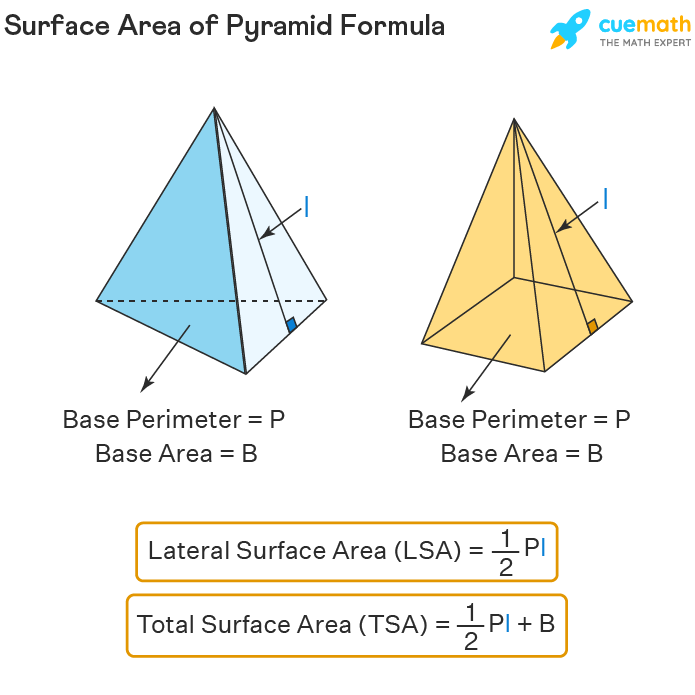
Pyramid Surface Area Formula
The surface area of a pyramid can be calculated using the formula: Surface Area = Base Area + Lateral Area. To find the lateral area, you can use the formula:
Lateral Area = (Perimeter of Base × Slant Height) / 2
The slant height is the distance from the apex of the pyramid to the midpoint of an edge of the base, which differs from the height of the pyramid. This formula is particularly useful when considering the construction and design of pyramidal structures, where maximizing surface area can enhance structural stability and aesthetic appeal.
Volume of a Pyramid Formula
Another significant aspect of working with pyramids is grasping the volume, represented by the formula Volume = (Base Area × Height) / 3. Understanding volume calculations is vital in fields like architecture and engineering, where knowledge of physical space usage is essential.
Consider a practical case where you need to determine how much material is required to build a rectangular pyramid. By calculating both the base area and height, you can then easily determine the total volume, allowing you to estimate costs and resource needs effectively.
Advanced Techniques for Area Calculation
Once you’re comfortable with the basic calculations, exploring advanced techniques ensures a deeper understanding of area calculation in pyramids. From variations in shape to methods of visualizing geometry, these approaches can enhance your calculations and architectural designs.
Understanding Oblique Pyramids
Oblique pyramids differ from right pyramids as their apex is not directly above the center of the base. Despite this, the calculation for both surface area and volume remains similar, with adjustments made for slant height calculations based on the vertex angle. Properly visualizing these characteristics assists architects and builders in creating designs that conform to specific aesthetic and functional needs.
Practical Uses of Pyramid Geometry
Pyramids are prevalent in architecture, and recognizing their importance can direct how we design modern structures. Utilizing models and pyramid designs can aid in understanding structural stability and weight distribution, which is crucial in large architectural projects. Engineers must adeptly use geometry to visualize potential outcomes and ensure that their constructions adhere to safety regulations.
Simplifying Complex Pyramid Calculations
Using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) modeling software can streamline the calculation process, allowing for accurate representations of complex pyramid shapes. Whether you are designing a commercial structure that incorporates pyramidal elements or exploring artistic representations of pyramids, CAD tools help simulate multiple designs while providing quick calculations for areas and volumes.
Conclusion and Key Takeaways
Calculating the area of a pyramid, and understanding the properties that shape its calculation, is pivotal in geometry and various real-world applications. The five methods outlined include:
- Methodical base area calculations tailored for each base type.
- Employing the pyramid surface area formula effectively.
- Utilizing the volume formula for practical architecture designs.
- Exploring the dynamics of oblique pyramids.
- Taking advantage of modern CAD modeling for complex shapes.
With strong foundational knowledge and application of techniques, you can confidently tackle any pyramid area calculation. For further exploration, check additional resources on [geometry of pyramids](https://dietpure.info/?p=824) and [volume calculations](https://dietpure.info/?p=819).
FAQ
1. What is the difference between a triangular pyramids and square pyramids in terms of area calculation?
Triangular pyramids have a triangular base, while square pyramids have a square base. Their area calculations differ primarily in how base areas are computed using respective formulas. This difference influences the overall surface area and volume, making a clear understanding of each shape’s properties essential in geometry.
2. How do I calculate the lateral area of a pyramid?
The lateral area of a pyramid can be calculated by the formula: Lateral Area = (Perimeter of Base × Slant Height) / 2. Be sure to measure the slant height accurately, as it’s the key to their lateral dimensions in pyramid design and structural analysis.
3. Why is the height of a pyramid significant?
The height of a pyramid determines both the volume and the overall capacity of the pyramid. Understanding how height influences these calculations allows you to accurately model materials and resources needed for construction or design projects that incorporate pyramidal shapes.
4. Can I simplify pyramid area calculations using software?
Yes! Utilizing CAD software can greatly simplify pyramid area and volume calculations by offering accurate modeling and design simulations. This aids in visualizing different types of pyramids and understanding how adjustments in dimensions affect overall surface area and structural integrity.
5. What are some practical uses for the knowledge of pyramid geometry?
The applications of pyramid geometry are vast, ranging from architectural design to historical studies. Understanding the properties and calculations of pyramids can enhance structural stability in buildings, while also contributing to artistic representations in modern design. Knowledge of pyramids also plays a crucial role in educational settings, allowing deeper exploration of geometric principles and problem-solving strategies.
“`